
Refrigeration Cycle of a Heat Pump in Cooling Mode! YouTube
Heat pumps are fantastic, all-electric options for heating applications. Advancements in VRF technology have increased the viability of heat pumps over traditional fuel-fired heating equipment. This article will explore the fundamentals of the heat pump cycle, emphasizing the effect of refrigerant type and operating pressure on the cooling and heating performance, the sizing procedure for air.
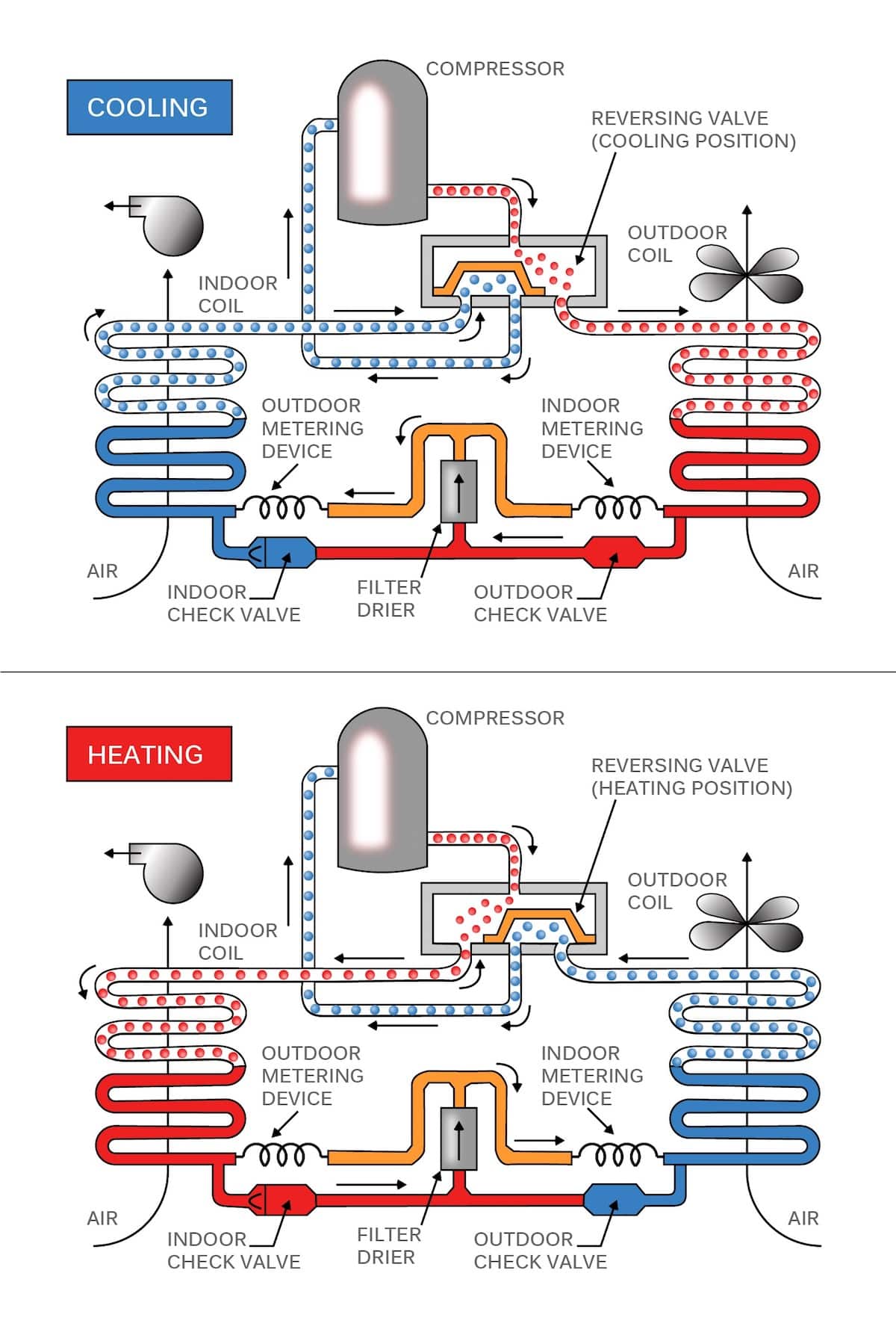
Heat Pump Refrigerant Flow Chart
e. Thermodynamic heat pump cycles or refrigeration cycles are the conceptual and mathematical models for heat pump, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. A heat pump is a mechanical system that transmits heat from one location (the "source") at a certain temperature to another location (the "sink" or "heat sink") at a higher temperature. [1]
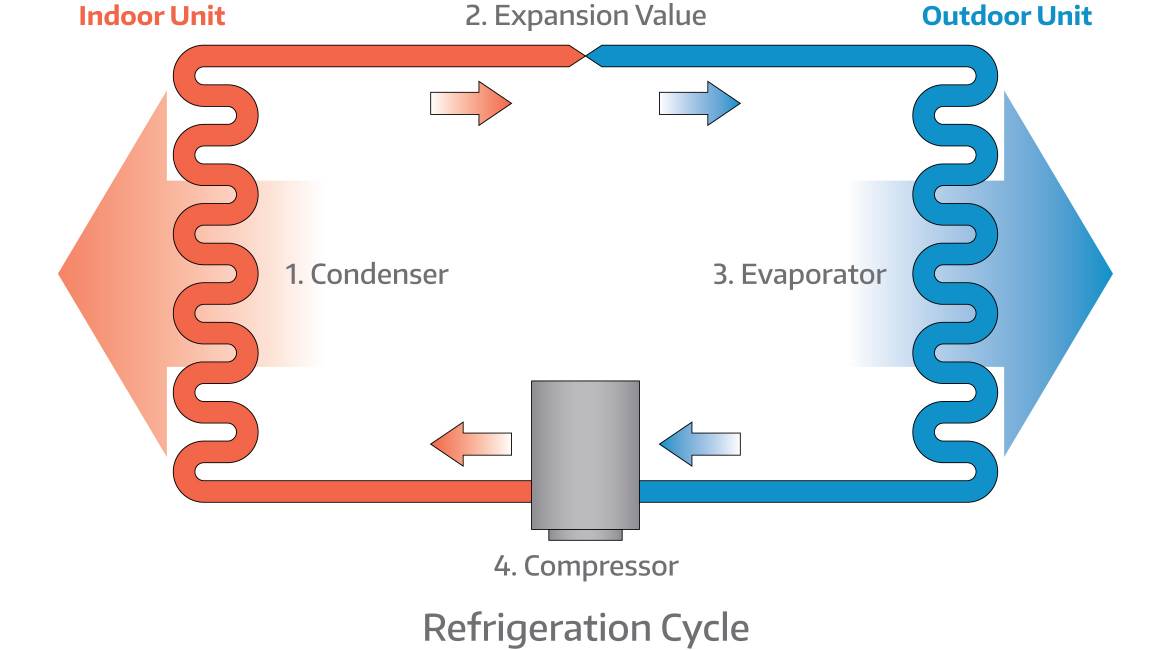
refrigerationcycle Real Refrigeration
Figure 12.13 (a) Heat transfer to the gas in a cylinder increases the internal energy of the gas, creating higher pressure and temperature. (b) The force exerted on the movable cylinder does work as the gas expands. Gas pressure and temperature decrease during expansion, indicating that the gas's internal energy has decreased as it does work.

The Refrigeration Cycle In easy to understand descriptions & diagrams!
Carbon dioxide was one of the fist refrigerants in the earliest heat pump and refrigeration systems, but ended up replaced by synthetic refrigerants after 1930s, and now renewed for its safe, economic and environmentally sustainable characteristics especially used in transcritical cycles. To overcome limitations imposed by CO 2 's low critical.

Heat Engine Carnot Cycle Heat Pump and Refrigeration Cycle Thermodynamics YouTube
Figure 15.5.3 15.5. 3: A simple heat pump has four basic components: (1) condenser, (2) expansion valve, (3) evaporator, and (4) compressor. In the heating mode, heat transfer Qc Q c occurs to the working fluid in the evaporator (3) from the colder outdoor air, turning it into a gas. The electrically driven compressor (4) increases the.
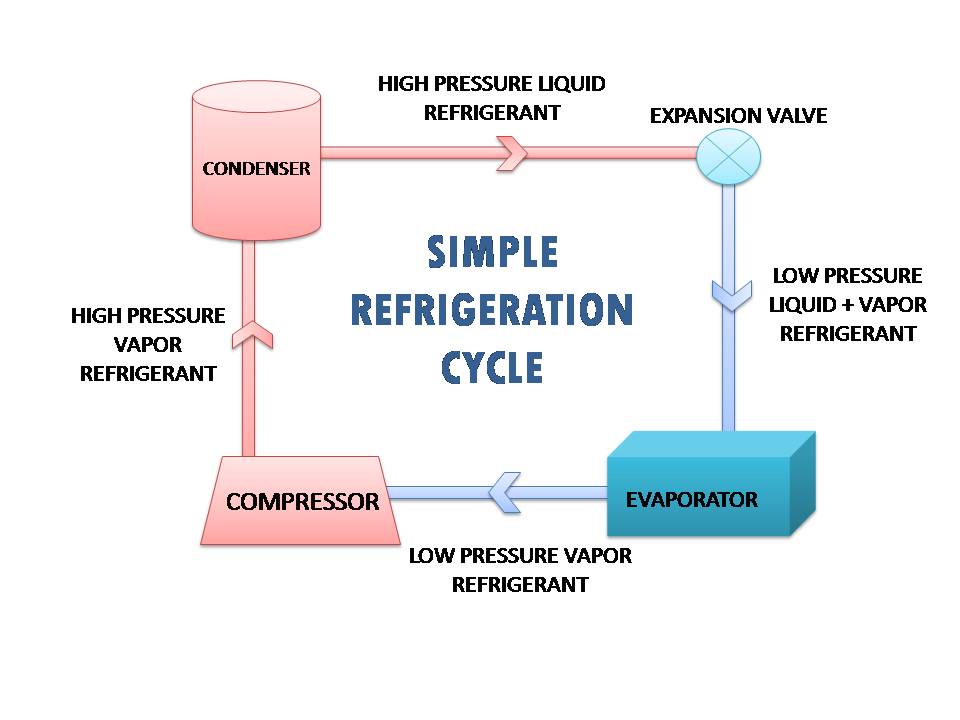
The 4 Main Important Components of Refrigeration Cycle
Example 7.9.1 7.9. 1. The measured performance of a power cycle indicates that the heat transfer into the cycle is 800 kJ/cycle 800 k J / c y c l e and the heat transfer out of the cycle is 600 kJ/cycle 600 k J / c y c l e. Determine the thermal efficiency of this power cycle. Solution.

6.2 Refrigerator and heat pump Introduction to Engineering Thermodynamics
82183. Heat pumps are devices that operate in a cycle similar to the vapor-compression refrigerator cycle illustrated in Figure 1. In its most basic form, a vapor-compression refrigeration system [see Van Wylen (1985)] consists of an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser, a throttling device which is usually an expansion valve or capillary tube.

Schematic diagram of an absorption refrigeration cycle; A absorber, C... Download Scientific
In the refrigeration cycle, there are five basic components: a fluid refrigerant, a compressor, a condenser coil, an evaporator coil, and an expansion device. The compressor constricts the refrigerant vapour, raising its pressure, and pushes it into the coils on the outside of the refrigerator.. A heat pump is a mechanical compression cycle.
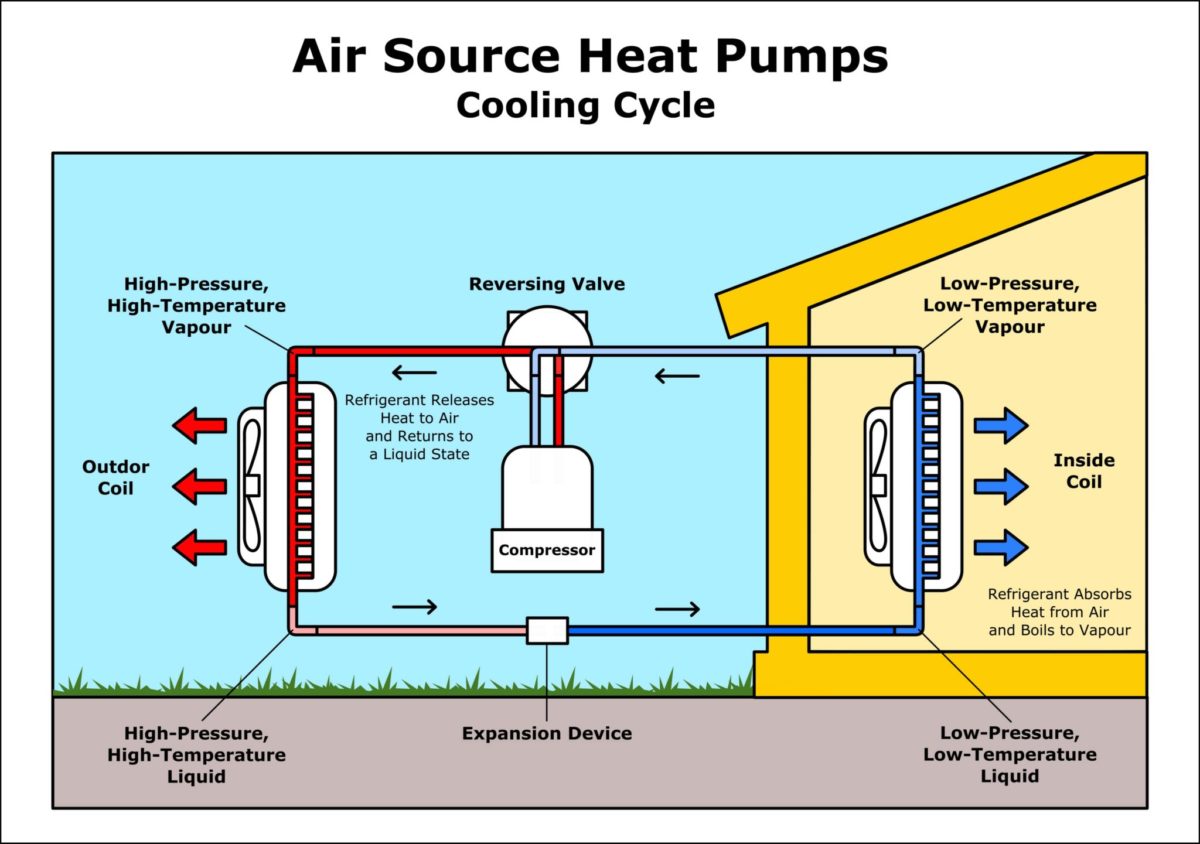
What Is a Heat Pump and How Does It Work?
A heat pump cycle diagram graphically represents the four main stages of the heat pump operation: evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion. Each of these stages plays a crucial role in moving heat from a cooler area to a warmer one, or vice versa, depending on the desired effect (heating or cooling).

The refrigeration cycle for a heat pump in heating mode Energy Vanguard
An air-source heat pump uses advanced technology and the refrigeration cycle to heat and cool your home. This allows a heat pump to provide year-round indoor comfort - no matter what the season is. Heat Pump in Air Conditioning Mode. When properly installed and functioning, a heat pump can help maintain cool, comfortable temperatures while reducing humidity levels inside your home.
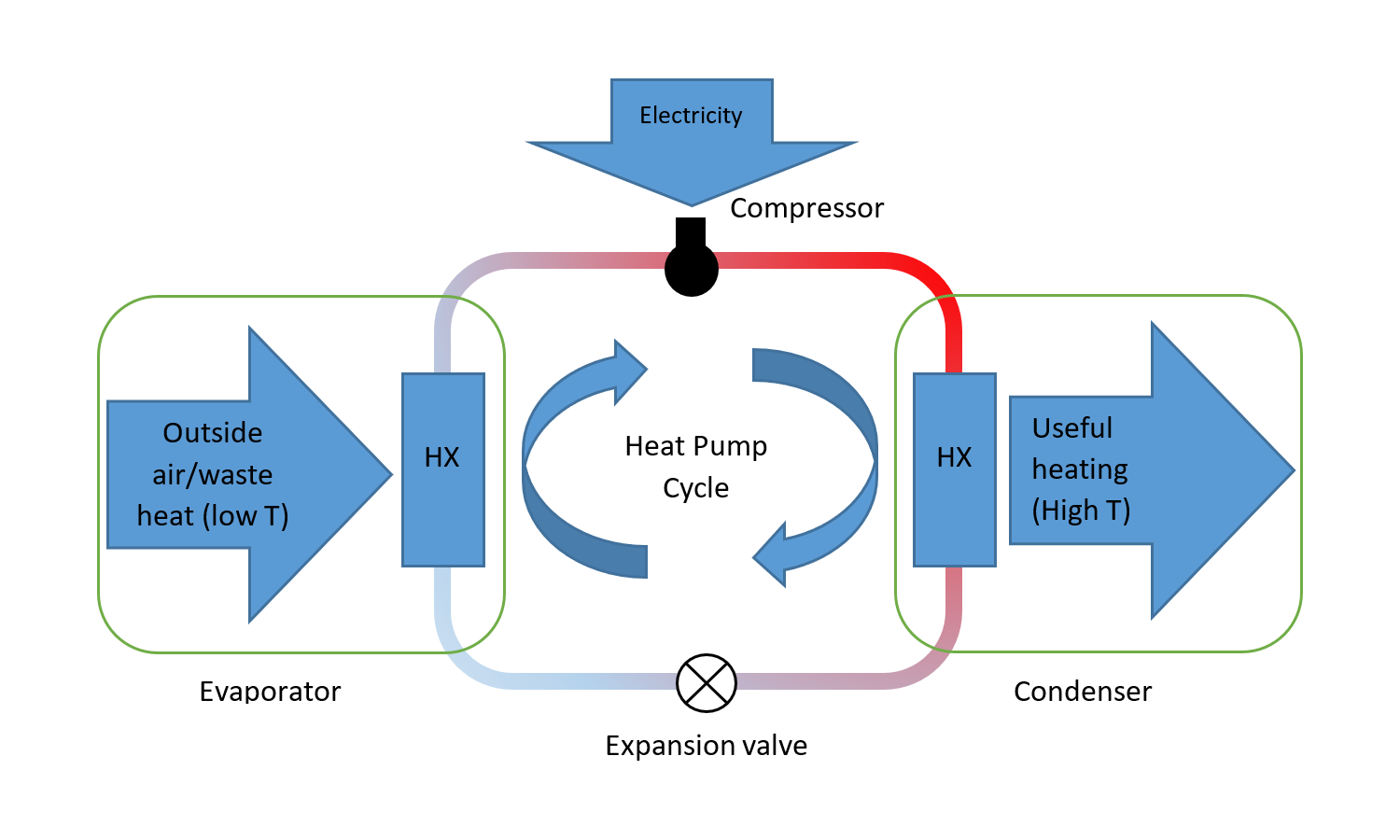
Heat Pumps Explained
December 20, 2023 by TechieScience Core SME. Heat pumps and refrigeration cycles are essential components in various heating and cooling systems. These systems work on the principle of transferring heat from one place to another using a refrigerant. Heat pumps are commonly used in both residential and commercial settings to provide efficient.
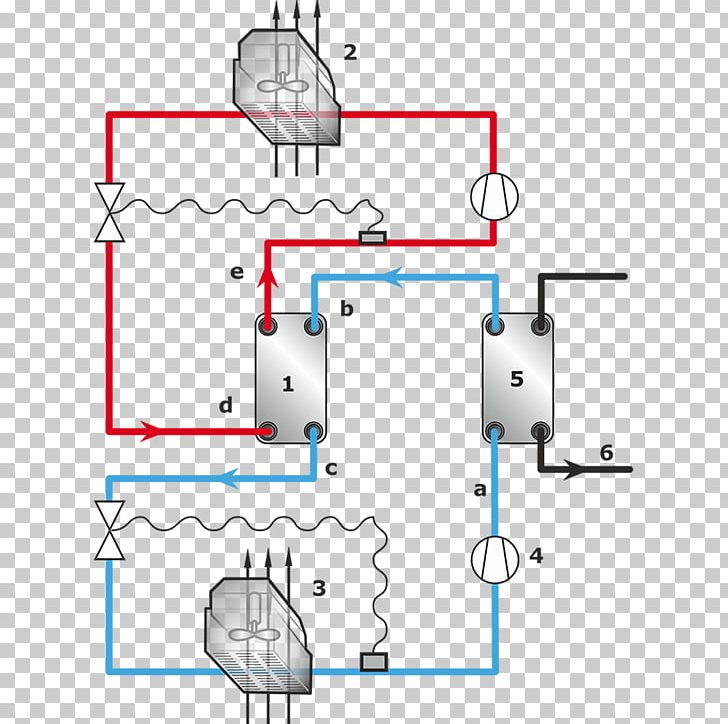
Diagram Heat Pump And Refrigeration Cycle System Schematic PNG, Clipart, Angle, Area, Chiller
Heat pump refrigeration cycle - Function and basic principle. It sounds contradictory: What does a refrigeration cycle do in a heat pump? Resolving precisely this apparent contradiction is the key to understanding the fundamentals and functioning of refrigeration cycles - and heat pumps.

SOLUTION Heat pump and refrigeration cycle Studypool
In this project three heat pump water heaters were evaluated. One system was an integrated package with the heat pump compressor and evaporator mounted on top of the hot water tank and the condenser formed from a wrap-around coil on the tank as shown in Fig. 1.This system relies on natural convection of water in the tank over the condenser wall and hence avoids the parasitic energy losses.

HVAC/R Refrigerant Cycle Basics HVAC School (2022)
Either a refrigerator or a heat pump is an engine running in reverse. For a refrigerator, the focus is on removing heat from a specific area. For a heat pump, the focus is on dumping heat to a specific area. We first consider a refrigerator (Figure 4.4.1 4.4. 1 ). The purpose of this engine is to remove heat from the cold reservoir, which is.

Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics Lec 6, pt 4 of 4 Refrigerators and Heat Pumps YouTube
A heat pump uses the same vapour compression refrigeration cycle, see Figure 6.2.1, as a refrigerator. It absorbs heat from a heat sink (e.g., outdoor air in the winter) and delivers (more) heat to a heat source (e.g., indoor air) by consuming work. Applying the first law of thermodynamics to the heat pump cycle, we can derive.

HVAC Refrigeration Cycle Diagram
The cycles we used to describe the engine in the preceding section are all reversible, so each sequence of steps can just as easily be performed in the opposite direction. In this case, the engine is known as a refrigerator or a heat pump, depending on what is the focus: the heat removed from the cold reservoir or the heat dumped to the hot.
- The Place Beyond The Pines Trailer
- Wat Is Taylor Swift Haar Lievelingskleur
- Flights From Dublin To United States
- Hoeveel Stemmen Nodig Voor Top 2000
- Boruto Two Blue Vortex Release Date
- Hoeveel Continenten Zijn Er In De Wereld
- 1999 Rf 10 Euro Cent
- Te Conserveren Inkomen Pensioen Opvragen
- Texas Instrument Calculator Ti 84
- Isla Bocas Del Toro Panama