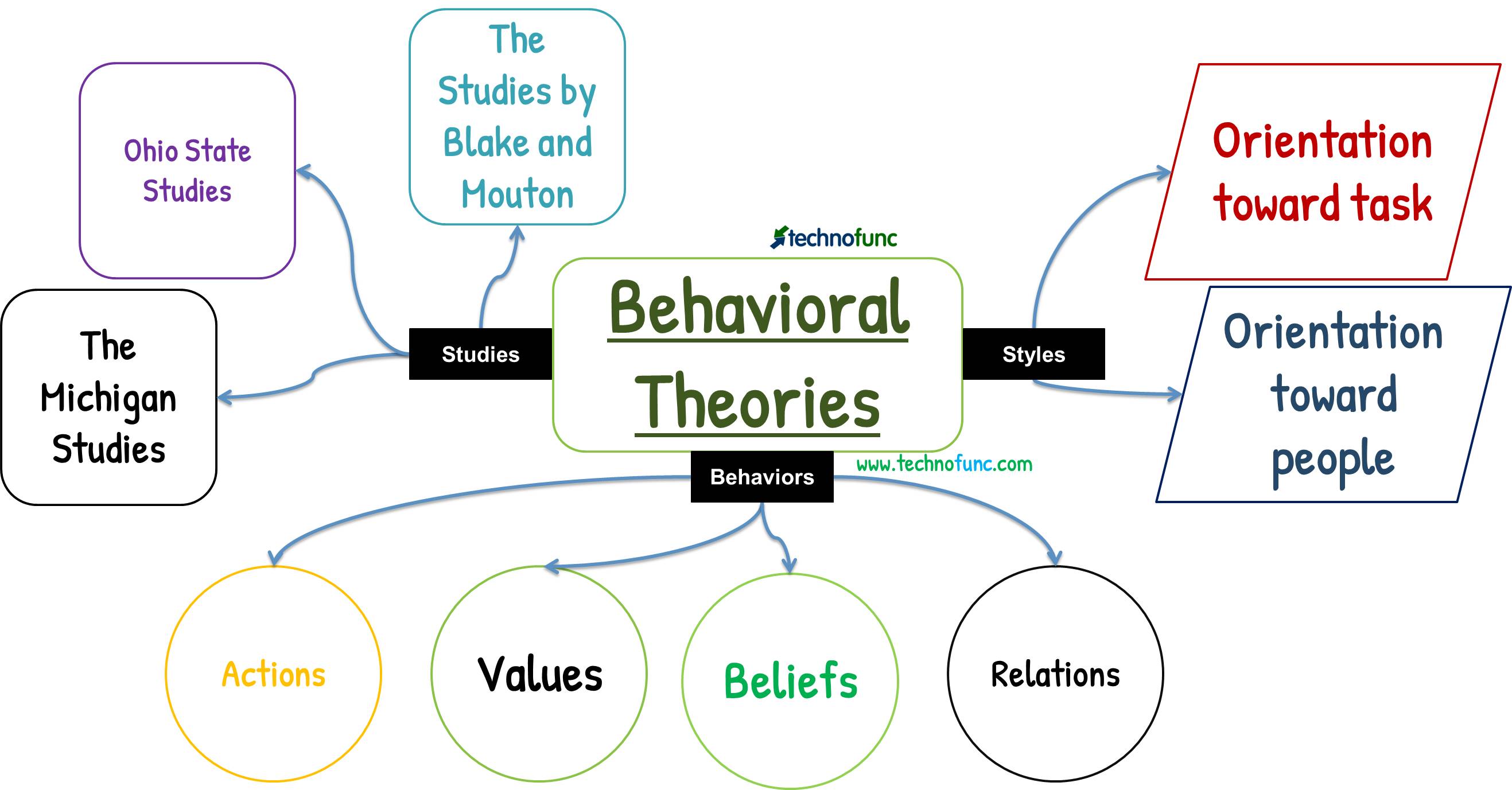
BUS 440 Reading Behavioral Theories of Leadership ILC
Please see the Notice of Retraction.The Behavioral Theory of the Firm provides a well-evidenced perspective on organizational decision making that has influenced a wide array of literatures, including the substantial body of work on organizational change. This literature suggests that organizations are more likely to undertake major changes when their performance declines below aspirations or.
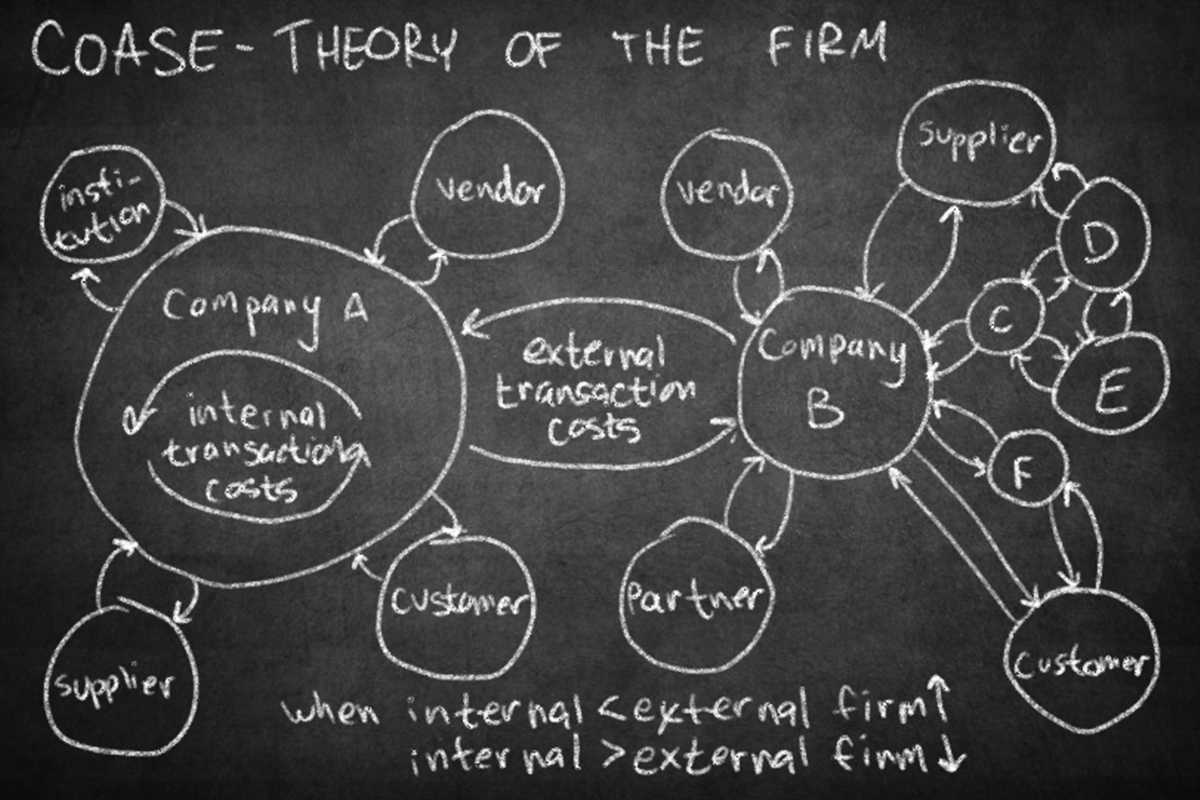
Theory of the Firm Razorhorse
The Behavioral Theory of the Firm has had an enormous influence on organizational theory, strategic management, and neighboring fields of socio-scientific inquiry. Its central concepts have become foundational to any theoretical and empirical work focussed on organizational phenomena. Unlike past reviews of this work, we start by focusing less.

PPT Economic Foundations of Strategy Chapter 1 Behavioral Theory of the Firm PowerPoint
Quick Reference. Theories of firm behaviour based on considering the objectives of individuals and groups within firms. In contrast to orthodox models of the firm based on the assumption of profit maximization, with some allowance for risk aversion, behavioural models consider the motives of managers and other groups within the firm.
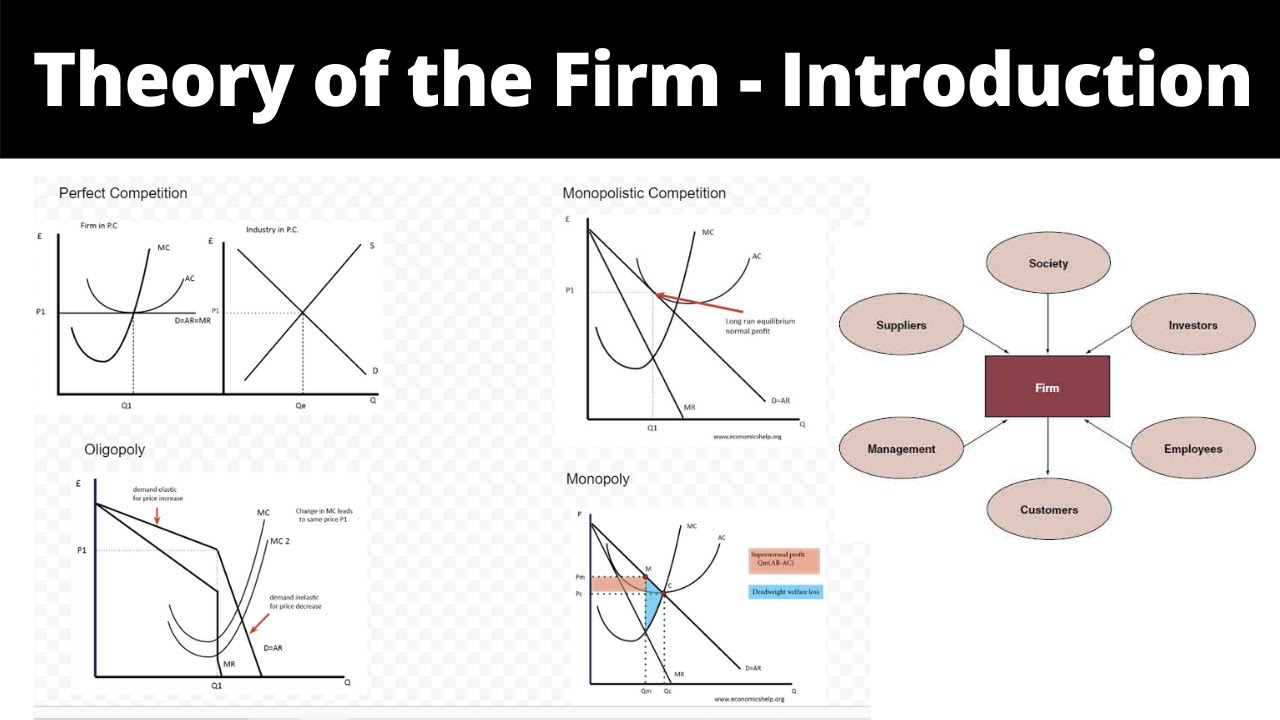
Theory of the Firm Introduction YouTube
Richard M. Cyert, James G. March. Wiley, Jul 27, 1992 - Business & Economics - 268 pages. Behavioural Theory of the Firm has become a classic work in organizational theory, and is one of the most significant contributions to improving the theory of the firm. This second edition includes new material which puts the original text in a.

PPT Economic Foundations of Strategy Chapter 1 Behavioral Theory of the Firm PowerPoint
The behavioral theory of the firm first appeared in the 1963 book A Behavioral Theory of the Firm by Richard M. Cyert and James G. March. The work on the behavioral theory started in 1952 when March, a political scientist, joined Carnegie Mellon University, where Cyert was an economist.. Before this model was formed, the existing theory of the firm had two main assumptions: profit maximization.

Understanding Theory of the Firm YouTube
The "behavioral theory of the firm" refers to a research tradition that follows the basic assumptions and interests of Richard M. Cyert and James G. March's pioneering work, A Behavioral Theory of the Firm ( Cyert and March 1963, cited under Classic Treatments ). This work examines how organizations function when managers have bounded.

A retrospective look at A Behavioral Theory of the Firm Journal of Economic Behavior & Studocu
A Behavioral Theory of the Firm has become a classic work in organizational theory, looking inside the firm to develop new theoretical ideas about economic behavior.The second edition reaffirms the seminal arguments and insights of the first and puts the original text in its contemporary context. Rejecting the portrayal of the firm found in classical economic theory, the authors focus on the.

Behavioural Theories of the Firm Economics tutor2u
The Behavioral Theory of the Firm has had an enormous influence on organizational theory, strategic management, and neighboring fields of socio-scientific inquiry. Its central concepts have become foundational to any theoretical and empirical work focussed on organizational phenomena. Unlike past reviews of this work, we start by focusing less on reviewing these concepts than we do on.

Behavioural Theories of The Firm Economics Economies
Abstract. Provides a theory of decision making within business organizations. Contrary to the economic theory of the firm, which sees firms as profit-maximizing entities, the authors advocate a theory based on empirical observation of actual firm decision-making. Various features of firm decision-making are identified.

Behavioural Theories of the Firm [PPT Powerpoint]
The Behavioral Theory of the Firm has had an enormous influence on organizational theory, strategic management, and neighboring fields of socio-scientific inquiry. Its central concepts have become foundational to any theoretical and empirical work focussed on organizational phenomena. Unlike past reviews of this work, we start by focusing less on reviewing these concepts than we do on.

A Behavioral Theory of the Firm Cyert, Richard Michael 1921 Libros
Behavioral Theory of the Firm T he chapter begins with Barnard's (1938) The Functions of the Executive and is followed by four books from the Carnegie School: Simon's (1947) Administrative Behavior,March and Simon's (1958) Organizations, Cyert and March's (1963) A Behavioral Theory of the Firm, and Simon's (1982) Models of Bounded Rationality: Behavioral

Behavioural Theories of the Firm [PPT Powerpoint]
Citation. Cyert, R. M., & March, J. G. (1963). A behavioral theory of the firm. Prentice Hall/Pearson Education.

Behavioural theory
In classical economics, the theory of firms is based on the assumption that they will seek profit maximisation. However, in the real world managers and owners may behave quite differently. Behavioural Theories of the Firm include: Size of a firm/prestige. Some managers may simply aim for working in a big and seemingly successful firm which.

Behavioral Theory Of The Firm, Richard Cyert 9780631174516 Boeken bol
In this introductory piece, we take stock of the impact of Cyert and March's A Behavioral Theory of the Firm, describe current research trends in the behavioral tradition, and introduce the special issue's papers.A Behavioral Theory of the Firm is one of the most influential management books of all time. In the book, Cyert and March developed theoretical building blocks that became the.

A Behavioral Theory of the Firm (Cyert and March, 1963)
A behavioral theory of the firm by Cyert, Richard Michael, 1921-Publication date 1963 Topics Decision-making -- Mathematical models, Industrial management -- Mathematical models Publisher Englewood Cliffs, N.J. : Prentice-Hall Collection printdisabled; trent_university; internetarchivebooks Contributor Internet Archive

(PDF) Behavioural Theory of the Firm
Behavioural theory of the firm. From the perspective of the BTOF, it is the discrepancy between aspiration and performance that guides the strategic behaviour of firms (Fiegenbaum, Hart and Schendel, 1996). Cyert and March indicate that organizational action is determined by comparing realized goal variables to their aspirational levels. Goal.